News regarding the Secure socket layer...how it works
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is the standard security technology for establishing an encrypted link between a web server and a browser. This link ensures that all data passed between the web server and browsers remain private and integral. SSL is an industry standard and is used by millions of websites in the protection of their online transactions with their customers.
To be able to create an SSL connection a web server requires an SSL Certificate. When you choose to activate SSL on your web server you will be prompted to complete a number of questions about the identity of your website and your company. Your web server then creates two cryptographic keys - a Private Key and a Public Key.
The Public Key does not need to be secret and is placed into a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) - a data file also containing your details. You should then submit the CSR. During the SSL Certificate application process, the Certification Authority will validate your details and issue an SSL Certificate containing your details and allowing you to use SSL. Your web server will match your issued SSL Certificate to your Private Key. Your web server will then be able to establish an encrypted link between the website and your customer's web browser.
The complexities of the SSL protocol remain invisible to your customers. Instead their browsers provide them with a key indicator to let them know they are currently protected by an SSL encrypted session - the lock icon in the lower right-hand corner, clicking on the lock icon displays your SSL Certificate and the details about it. All SSL Certificates are issued to either companies or legally accountable individuals.
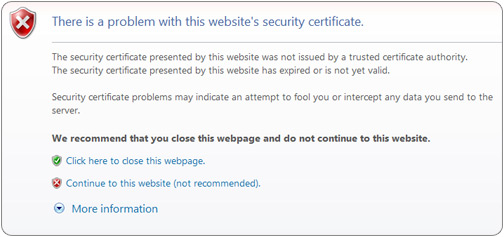
Typically an SSL Certificate will contain your domain name, your company name, your address, your city, your state and your country. It will also contain the expiration date of the Certificate and details of the Certification Authority responsible for the issuance of the Certificate. When a browser connects to a secure site it will retrieve the site's SSL Certificate and check that it has not expired, it has been issued by a Certification Authority the browser trusts, and that it is being used by the website for which it has been issued. If it fails on any one of these checks the browser will display a warning to the end user letting them know that the site is not secured by SSL.
SSL (pronounced as separate letters) is short for Secure SocketsLayer, a protocol developed by Netscape for transmitting private documents via the Internet. SSL uses a cryptographic system that uses two keys to encrypt data − a public key known to everyone and a private or secret key known only to the recipient of the message. Both Netscape Navigator and Internet Explorer support SSL, and many Web sites use the protocol to obtain confidential user information, such as credit card numbers. By convention, URLs that require an SSL connection start with https: instead of http:.
Another protocol for transmitting data securely over the World Wide Web is Secure HTTP (S-HTTP). Whereas SSL creates a secure connection between a client and a server, over which any amount of data can be sent securely, S-HTTP is designed to transmit individual messages securely. SSL and S-HTTP, therefore, can be seen as complementary rather than competing technologies. Both protocols have been approved by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as a standard.
General Web Users with SSL Certificate Problems
Digital certificates provide security to websites by encrypting sensitive data and verfying the identity of the websites that are secured.
We provide these certificates as a service to website owners to ensure the security of online communications.
SSL problem messages and warnings are often displayed in an attempt to protect website users from potentially compromising situations. However, an SSL error message may also indicate a problem that is entirely innocuous in nature. In this second case, there is often an issue either with the website you are connecting to or even possibly a misconfiguration on your own end.
If you ever encounter an SSL related warning (such as a security certificate mismatch, certificate not trusted, or secure and non-secure items, see below), you may want to hold off on entering your login details or credit card information until you can make sure you are not in a compromising online situation.
Learn to Protect Against SSL Fraud
To resolve a problem that you may be having, the first thing that you want to check is that your computer's time and date are accurate. Because expired or not-yet-valid security certificates throw up warnings, having the date on your machine wrong could potentially cause security errors on many secure sites that you access.
Additionally, if you have recently enabled new secure settings in a website, try disabling those settings and seeing if the warning messages go away. While this is not fix, it can give you a point to work from when communicating with the website owner to help them know how to fix the problems.
One of the best things you can do if you encounter an error is to find a third-party source for a phone number of the organization whose website you are on and try calling the organization to let them know about the issue, or to try to handle whatever business you needed to handle with them over the phone. If they are having a problem on their end, they should be able to fix it so other users are not inconvenienced.
If you are having a problem with the website of a large corporation that may be difficult to reach by telephone, make sure to exercise discretion and never enter personal information in a website that throws an SSL error message.
Website Administrators & Fixing an SSL Problem
We offer a variety of tools for website administrators to investigate and troubleshoot potential SSL problems.
- Start with our SSL diagnostic online tool to check your installation for issues.
- If you are using a Windows based server, you can use our Windows SSL Utility to resolve the most common certificate problems.
- Otherwise, if you just need help installing your certificate or creating a CSR, check out our SSL setup instruction guide.
- If none of that gets the job done, try checking out our list of additional certificate issues.
Guide to SSL Problem Fixing for Users and Administrators
If you are a DigiCert customer and encounter any SSL problem that you cannot resolve using the instructions on this page, feel free to give us a call today for live support!
T he types of ssl errors
SSL Error Codes
Table 8.1 Error codes defined in sslerr.h
| Constant | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SSL_ERROR_EXPORT_ONLY_SERVER | -12288 | "Unable to communicate securely. Peer does not support high-grade encryption." The local system was configured to support the cipher suites permitted for domestic use. The remote system was configured to support only the cipher suites permitted for export use. |
| SSL_ERROR_US_ONLY_SERVER | -12287 | "Unable to communicate securely. Peer requires high-grade encryption which is not supported." The remote system was configured to support the cipher suites permitted for domestic use. The local system was configured to support only the cipher suites permitted for export use. |
| SSL_ERROR_NO_CYPHER_OVERLAP | -12286 | "Cannot communicate securely with peer: no common encryption algorithm(s)." The local and remote systems share no cipher suites in common. This can be due to a misconfiguration at either end. It can be due to a server being misconfigured to use a non-RSA certificate with the RSA key exchange algorithm. |
| SSL_ERROR_NO_CERTIFICATE | -12285 | "Unable to find the certificate or key necessary for authentication." This error has many potential causes; for example: Certificate or key not found in database. Certificate not marked trusted in database and Certificate's issuer not marked trusted in database. |
| SSL_ERROR_BAD_CERTIFICATE | -12284 | "Unable to communicate securely with peer: peers's certificate was rejected." A certificate was received from the remote system and was passed to the certificate authentication callback function provided by the local application. That callback function returned SECFailure, and the bad certificate callback function either was not configured or did not choose to override the error code returned by the certificate authentication callback function. |
| -12283 | (unused) | |
| SSL_ERROR_BAD_CLIENT | -12282 | "The server has encountered bad data from the client." This error code should occur only on sockets that are acting as servers. It is a generic error, used when none of the other more specific error codes defined in this file applies. |
| SSL_ERROR_BAD_SERVER | -12281 | "The client has encountered bad data from the server." This error code should occur only on sockets that are acting as clients. It is a generic error, used when none of the other more specific error codes defined in this file applies. |
| SSL_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED_CERTIFICATE_TYPE | -12280 | "Unsupported certificate type." The operation encountered a certificate that was not one of the well known certificate types handled by the certificate library. |
| SSL_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED_VERSION | -12279 | "Peer using unsupported version of security protocol." On a client socket, this means the remote server has attempted to negotiate the use of a version of SSL that is not supported by the NSS library, probably an invalid version number. On a server socket, this means the remote client has requested the use of a version of SSL older than version 2. |
| -12278 | (unused) | |
SSL_ERROR_WRONG_CERTIFICATE | -12277 | "Client authentication failed: private key in key database does not correspond to public key in certificate database." |
| SSL_ERROR_BAD_CERT_DOMAIN | -12276 | "Unable to communicate securely with peer: requested domain name does not match the server's certificate." This error code should be returned by the certificate authentication callback function when it detects that the Common Name in the remote server's certificate does not match the hostname sought by the local client, according to the matching rules specified for CERT_VerifyCertName. |
SSL_ERROR_POST_WARNING | -12275 | (unused) |
| SSL_ERROR_SSL2_DISABLED | -12274 | "Peer only supports SSL version 2, which is locally disabled." The remote server has asked to use SSL version 2, and SSL version 2 is disabled in the local client's configuration. |
| SSL_ERROR_BAD_MAC_READ | -12273 | "SSL received a record with an incorrect Message Authentication Code." This usually indicates that the client and server have failed to come to agreement on the set of keys used to encrypt the application data and to check message integrity. If this occurs frequently on a server, an active attack (such as the "million question" attack) may be underway against the server. |
| SSL_ERROR_BAD_MAC_ALERT | -12272 | "SSL peer reports incorrect Message Authentication Code." The remote system has reported that it received a message with a bad Message Authentication Code from the local system. This may indicate that an attack on that server is underway. |
| SSL_ERROR_BAD_CERT_ALERT | -12271 | "SSL peer cannot verify your certificate." The remote system has received a certificate from the local system, and has rejected it for some reason. |
| SSL_ERROR_REVOKED_CERT_ALERT | -12270 | "SSL peer rejected your certificate as revoked." The remote system has received a certificate from the local system, and has determined that the certificate has been revoked. |
| SSL_ERROR_EXPIRED_CERT_ALERT | -12269 | "SSL peer rejected your certificate as expired." The remote system has received a certificate from the local system, and has determined that the certificate has expired. |
| SSL_ERROR_SSL_DISABLED | -12268 | "Cannot connect: SSL is disabled." The local socket is configured in such a way that it cannot use any of the SSL cipher suites. Possible causes include: (a) both SSL2 and SSL3 are disabled, (b) All the individual SSL cipher suites are disabled, or (c) the socket is configured to handshake as a server, but the certificate associated with that socket is inappropriate for the Key Exchange Algorithm selected. |
| SSL_ERROR_FORTEZZA_PQG | -12267 | "Cannot connect: SSL peer is in another FORTEZZA domain." The local system and the remote system are in different FORTEZZA domains. They must be in the same domain to communicate. |
| SSL_ERROR_UNKNOWN_CIPHER_SUITE | -12266 | "An unknown SSL cipher suite has been requested." The application has attempted to configure SSL to use an unknown cipher suite. |
| SSL_ERROR_NO_CIPHERS_SUPPORTED | -12265 | "No cipher suites are present and enabled in this program." Possible causes: (a) all cipher suites have been configured to be disabled, (b) the only cipher suites that are configured to be enabled are those that are disallowed by cipher export policy, (c) the socket is configured to handshake as a server, but the certificate associated with that socket is inappropriate for the Key Exchange Algorithm selected. |
| SSL_ERROR_BAD_BLOCK_PADDING | -12264 | "SSL received a record with bad block padding." SSL was using a Block cipher, and the last block in an SSL record had incorrect padding information in it. This usually indicates that the client and server have failed to come to agreement on the set of keys used to encrypt the application data and to check message integrity. If this occurs frequently on a server, an active attack (such as the "million question" attack) may be underway against the server. |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG | -12263 | "SSL received a record that exceeded the maximum permissible length." This generally indicates that the remote peer system has a flawed implementation of SSL, and is violating the SSL specification. |
| SSL_ERROR_TX_RECORD_TOO_LONG | -12262 | "SSL attempted to send a record that exceeded the maximum permissible length." This error should never occur. If it does, it indicates a flaw in the NSS SSL library. |
| SSL_ERROR_CLOSE_NOTIFY_ALERT | -12230 | "SSL peer has closed this connection." The local socket received an SSL3 alert record from the remote peer, reporting that the remote peer has chosen to end the connection. The receipt of this alert is an error only if it occurs while a handshake is in progress. |
| SSL_ERROR_PUB_KEY_SIZE_LIMIT_EXCEEDED | -12210 | "SSL Server attempted to use domestic-grade public key with export cipher suite." On a client socket, this error reports that the remote server has failed to perform an "SSL Step down" for an export cipher. It has sent a certificate bearing a domestic-grade public key, but has not sent a ServerKeyExchange message containing an export-grade public key for the key exchange algorithm. Such a connection cannot be permitted without violating U.S. export policies. On a server socket, this indicates a failure of the local library. |
| SSL_ERROR_NO_SERVER_KEY_FOR_ALG | -12206 | "Server has no key for the attempted key exchange algorithm." An SSL client has requested an SSL cipher suite that uses a Key Exchange Algorithm for which the local server has no appropriate public key. This indicates a configuration error on the local server. |
| SSL_ERROR_TOKEN_INSERTION_REMOVAL | -12205 | "PKCS #11 token was inserted or removed while operation was in progress." A cryptographic operation required to complete the handshake failed because the token that was performing it was removed while the handshake was underway. Another token may also have been inserted into the same slot. |
| SSL_ERROR_TOKEN_SLOT_NOT_FOUND | -12204 | "No PKCS#11 token could be found to do a required operation." A cryptographic operation required a PKCS#11 token with specific abilities, and no token could be found in any slot, including the "soft token" in the internal virtual slot, that could do the job. May indicate a server configuration error, such as having a certificate that is inappropriate for the Key Exchange Algorithm selected. |
SSL_ERROR_NO_COMPRESSION_OVERLAP | -12203 | "Cannot communicate securely with peer: no common compression algorithm(s)." |
SSL_ERROR_HANDSHAKE_NOT_COMPLETED | -12202 | "Cannot initiate another SSL handshake until current handshake is complete." |
SSL_ERROR_BAD_HANDSHAKE_HASH_VALUE | -12201 | "Received incorrect handshakes hash values from peer." |
SSL_ERROR_CERT_KEA_MISMATCH | -12200 | "The certificate provided cannot be used with the selected key exchange algorithm." |
SSL_ERROR_NO_TRUSTED_SSL_CLIENT_CA | -12199 | "No certificate authority is trusted for SSL client authentication." |
SSL_ERROR_SESSION_NOT_FOUND | -12198 | "Client's SSL session ID not found in server's session cache." |
Received a malformed (too long or short or invalid content) SSL handshake: All the error codes in the following block indicate that the local socket received an improperly formatted SSL3 handshake message from the remote peer. This probably indicates a flaw in the remote peer's implementation. | ||
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_HELLO_REQUEST | -12261 | "SSL received a malformed Hello Request handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_CLIENT_HELLO | -12260 | "SSL received a malformed Client Hello handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_SERVER_HELLO | -12259 | "SSL received a malformed Server Hello handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_CERTIFICATE | -12258 | "SSL received a malformed Certificate handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_SERVER_KEY_EXCH | -12257 | "SSL received a malformed Server Key Exchange handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_CERT_REQUEST | -12256 | "SSL received a malformed Certificate Request handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_HELLO_DONE | -12255 | "SSL received a malformed Server Hello Done handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_CERT_VERIFY | -12254 | "SSL received a malformed Certificate Verify handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_CLIENT_KEY_EXCH | -12253 | "SSL received a malformed Client Key Exchange handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_FINISHED | -12252 | "SSL received a malformed Finished handshake message." |
Received a malformed (too long or short) SSL record: All the error codes in the following block indicate that the local socket received an improperly formatted SSL3 record from the remote peer. This probably indicates a flaw in the remote peer's implementation. | ||
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_CHANGE_CIPHER | -12251 | "SSL received a malformed Change Cipher Spec record." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_ALERT | -12250 | "SSL received a malformed Alert record." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_HANDSHAKE | -12249 | "SSL received a malformed Handshake record." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_APPLICATION_DATA | -12248 | "SSL received a malformed Application Data record." |
Received an SSL handshake that was inappropriate for the current state: All the error codes in the following block indicate that the local socket received an SSL3 handshake message from the remote peer at a time when it was inappropriate for the peer to have sent this message. For example, a server received a message from another server. This probably indicates a flaw in the remote peer's implementation. | ||
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_HELLO_REQUEST | -12247 | "SSL received an unexpected Hello Request handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_CLIENT_HELLO | -12246 | "SSL received an unexpected Client Hello handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_SERVER_HELLO | -12245 | "SSL received an unexpected Server Hello handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_CERTIFICATE | -12244 | "SSL received an unexpected Certificate handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_SERVER_KEY_EXCH | -12243 | "SSL received an unexpected Server Key Exchange handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_CERT_REQUEST | -12242 | "SSL received an unexpected Certificate Request handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_HELLO_DONE | -12241 | "SSL received an unexpected Server Hello Done handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_CERT_VERIFY | -12240 | "SSL received an unexpected Certificate Verify handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_CLIENT_KEY_EXCH | -12239 | "SSL received an unexpected Client Key Exchange handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_FINISHED | -12238 | "SSL received an unexpected Finished handshake message." |
Received an SSL record that was inappropriate for the current state: All the error codes in the following block indicate that the local socket received an SSL3 record from the remote peer at a time when it was inappropriate for the peer to have sent this message. This probably indicates a flaw in the remote peer's implementation. | ||
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_CHANGE_CIPHER | -12237 | "SSL received an unexpected Change Cipher Spec record." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_ALERT | -12236 | "SSL received an unexpected Alert record." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_HANDSHAKE | -12235 | "SSL received an unexpected Handshake record." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNEXPECTED_APPLICATION_DATA | -12234 | "SSL received an unexpected Application Data record." |
Received record/message with unknown discriminant: All the error codes in the following block indicate that the local socket received an SSL3 record or handshake message from the remote peer that it was unable to interpret because the byte that identifies the type of record or message contained an unrecognized value. This probably indicates a flaw in the remote peer's implementation. | ||
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNKNOWN_RECORD_TYPE | -12233 | "SSL received a record with an unknown content type." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNKNOWN_HANDSHAKE | -12232 | "SSL received a handshake message with an unknown message type." |
| SSL_ERROR_RX_UNKNOWN_ALERT | -12231 | "SSL received an alert record with an unknown alert description." |
All the error codes in the following block indicate that the local socket received an SSL3 or TLS alert record from the remote peer, reporting some issue that it had with an SSL record or handshake message it received. (Some _Alert codes are listed in other blocks.) | ||
| SSL_ERROR_HANDSHAKE_UNEXPECTED_ALERT | -12229 | "SSL peer was not expecting a handshake message it received." |
| SSL_ERROR_DECOMPRESSION_FAILURE_ALERT | -12228 | "SSL peer was unable to successfully decompress an SSL record it received." |
| SSL_ERROR_HANDSHAKE_FAILURE_ALERT | -12227 | "SSL peer was unable to negotiate an acceptable set of security parameters." |
| SSL_ERROR_ILLEGAL_PARAMETER_ALERT | -12226 | "SSL peer rejected a handshake message for unacceptable content." |
| SSL_ERROR_UNSUPPORTED_CERT_ALERT | -12225 | "SSL peer does not support certificates of the type it received." |
| SSL_ERROR_CERTIFICATE_UNKNOWN_ALERT | -12224 | "SSL peer had some unspecified issue with the certificate it received." |
| SSL_ERROR_DECRYPTION_FAILED_ALERT | -12197 | "Peer was unable to decrypt an SSL record it received." |
| SSL_ERROR_RECORD_OVERFLOW_ALERT | -12196 | "Peer received an SSL record that was longer than is permitted." |
| SSL_ERROR_UNKNOWN_CA_ALERT | -12195 | "Peer does not recognize and trust the CA that issued your certificate." |
| SSL_ERROR_ACCESS_DENIED_ALERT | -12194 | "Peer received a valid certificate, but access was denied." |
| SSL_ERROR_DECODE_ERROR_ALERT | -12193 | "Peer could not decode an SSL handshake message." |
| SSL_ERROR_DECRYPT_ERROR_ALERT | -12192 | "Peer reports failure of signature verification or key exchange." |
| SSL_ERROR_EXPORT_RESTRICTION_ALERT | -12191 | "Peer reports negotiation not in compliance with export regulations." |
| SSL_ERROR_PROTOCOL_VERSION_ALERT | -12190 | "Peer reports incompatible or unsupported protocol version." |
| SSL_ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_SECURITY_ALERT | -12189 | "Server requires ciphers more secure than those supported by client." |
| SSL_ERROR_INTERNAL_ERROR_ALERT | -12188 | "Peer reports it experienced an internal error." |
| SSL_ERROR_USER_CANCELED_ALERT | -12187 | "Peer user canceled handshake." |
SSL_ERROR_NO_RENEGOTIATION_ALERT | -12186 | "Peer does not permit renegotiation of SSL security parameters." |
Unspecified errors that occurred while attempting some operation: All the error codes in the following block describe the operation that was being attempted at the time of the unspecified failure. These failures may be caused by the system running out of memory, or errors returned by PKCS#11 routines that did not provide meaningful error codes of their own. These should rarely be seen. (Certain of these error codes have more specific meanings, as described.) | ||
| SSL_ERROR_GENERATE_RANDOM_FAILURE | -12223 | "SSL experienced a failure of its random number generator." |
| SSL_ERROR_SIGN_HASHES_FAILURE | -12222 | "Unable to digitally sign data required to verify your certificate." |
| SSL_ERROR_EXTRACT_PUBLIC_KEY_FAILURE | -12221 | "SSL was unable to extract the public key from the peer's certificate." |
| SSL_ERROR_SERVER_KEY_EXCHANGE_FAILURE | -12220 | "Unspecified failure while processing SSL Server Key Exchange handshake." |
| SSL_ERROR_CLIENT_KEY_EXCHANGE_FAILURE | -12219 | "Unspecified failure while processing SSL Client Key Exchange handshake." |
| SSL_ERROR_ENCRYPTION_FAILURE | -12218 | "Bulk data encryption algorithm failed in selected cipher suite." |
| SSL_ERROR_DECRYPTION_FAILURE | -12217 | "Bulk data decryption algorithm failed in selected cipher suite." |
| SSL_ERROR_MD5_DIGEST_FAILURE | -12215 | "MD5 digest function failed." |
| SSL_ERROR_SHA_DIGEST_FAILURE | -12214 | "SHA-1 digest function failed." |
| SSL_ERROR_MAC_COMPUTATION_FAILURE | -12213 | "Message Authentication Code computation failed." |
| SSL_ERROR_SYM_KEY_CONTEXT_FAILURE | -12212 | "Failure to create Symmetric Key context." |
| SSL_ERROR_SYM_KEY_UNWRAP_FAILURE | -12211 | "Failure to unwrap the Symmetric key in Client Key Exchange message." |
| SSL_ERROR_IV_PARAM_FAILURE | -12209 | "PKCS11 code failed to translate an IV into a param." |
| SSL_ERROR_INIT_CIPHER_SUITE_FAILURE | -12208 | "Failed to initialize the selected cipher suite." |
| SSL_ERROR_SOCKET_WRITE_FAILURE | -12216 | "Attempt to write encrypted data to underlying socket failed." After the data to be sent was encrypted, the attempt to send it out the socket failed. Likely causes include that the peer has closed the connection. |
| SSL_ERROR_SESSION_KEY_GEN_FAILURE | -12207 | "Failed to generate session keys for SSL session." On a client socket, indicates a failure of the PKCS11 key generation function. On a server socket, indicates a failure of one of the following: (a) to unwrap the pre-master secret from the ClientKeyExchange message, (b) to derive the master secret from the premaster secret, (c) to derive the MAC secrets, cryptographic keys, and initialization vectors from the master secret. If encountered repeatedly on a server socket, this can indicate that the server is actively under a "million question" attack. |
SEC Error Codes
Table 8.2 Security error codes defined in secerr.h





No comments:
Post a Comment